 Genius Scan SDK
Genius Scan SDK
The scan flow consists of two screens that enable the user to capture and validate each page of its document:
If the multi-page mode is enabled, the user will repeat this interaction until they validate their batch of scan on the camera screen.

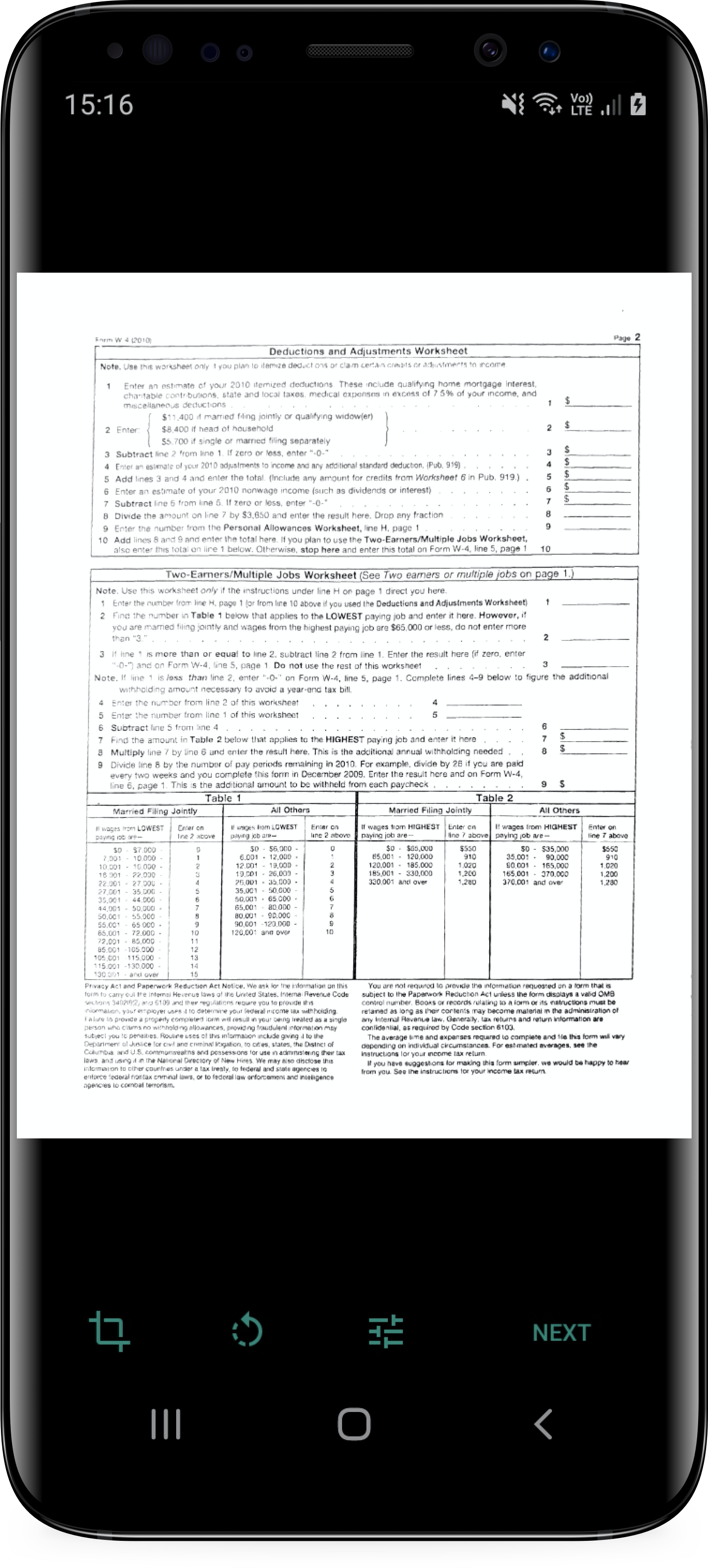
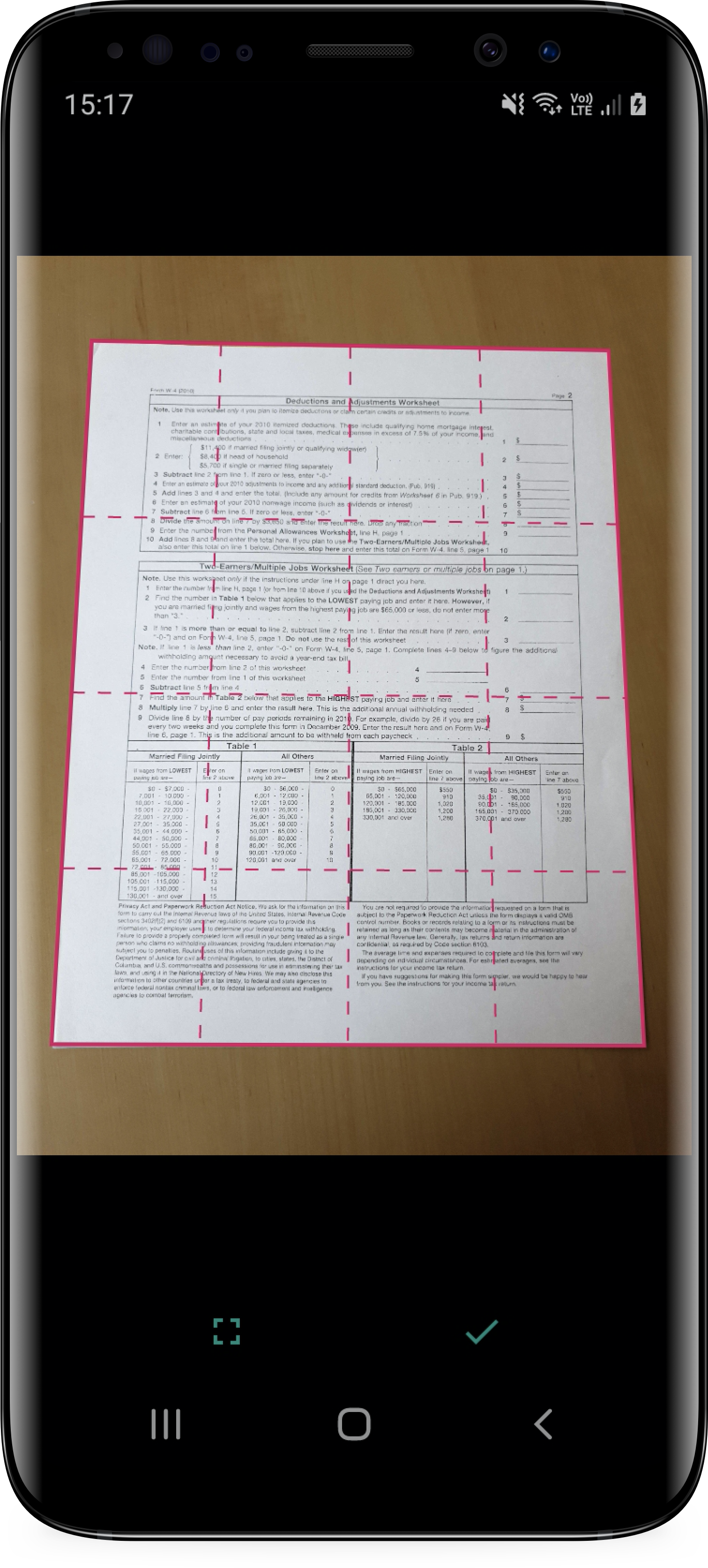
In this guide, you will learn how to integrate this simple scan flow with a couple of lines of code.
This guide assumes that you have followed the Getting Started guide :
gssdk-core and gssdk-scanflow libraries in your app with Gradle.You configure the scan flow with a configuration object, which lets you configure features such as:
All these parameters are extensively documented in the Android API documentation.
Once the user finishes their scan session, the scan flow returns the scanned pages’ list as images and a PDF file combining all the pages.
val scanConfiguration = ScanConfiguration().apply {
multiPage = true
}
ScanFlow.scanWithConfiguration(activity, scanConfiguration)
ScanConfiguration scanConfiguration = new ScanConfiguration();
scanConfiguration.multiPage = true;
ScanFlow.scanWithConfiguration(activity, scanConfiguration);
and… that’s it!
Implement the onActivityResult callback in the activity you used to start the scan flow and get a ScanResult using ScanFlow.getScanResultFromActivityResult. The result object will contain the PDF file as well as the images of the pages that were scanned.
override fun onActivityResult(requestCode: Int, resultCode: Int, data: Intent?) {
try {
val result = ScanFlow.getScanResultFromActivityResult(data)
// Do anything with the images or the PDF file
} catch (e: Exception) {
// There was an error during the scan flow. Check the exception for more details.
}
}
@Override
protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, @Nullable Intent data) {
try {
ScanResult result = ScanFlow.getScanResultFromActivityResult(data);
// Do anything with the images or the PDF file
} catch (Exception e) {
// There was an error during the scan flow. Check the exception for more details.
}
}
An implicit API contract is that you have to take ownership of the resulting files referenced by the `ScanResult object. You are responsible for moving them to the appropriate place and deleting them if you don’t need them anymore.
© 2024 The Grizzly Labs. All rights reserved.